213
213

Thanks to the invaluable feedback from our customers, we’ve transformed Chrom Quality Control (Chrom QC) into a significantly more powerful solution for automated quality checks on sample batches. Our dedicated team has applied their deep expertise to deliver enhanced capabilities and a refined user interface ensuring a smoother, more efficient experience for you.
Expanded Target Recognition and Peak Assignment
The new version of Chrom QC expands its capabilities for identifying and assigning peaks to either a consistent target across an entire batch of samples or to a unique target for each individual sample. Users can now choose from a broad selection of chromatograms, such as TIC, EIC, UV, PDA, BPC, and other trace types, and enjoy complete flexibility in selecting MS extraction functions, including injection parameters, polarity, and more.

It is now possible to define parameters for target recognition, allowing retention time (RT) to take precedence over other mass and structure-related information: m/z, molecular formula, SMILES and/or monoisotopic mass.
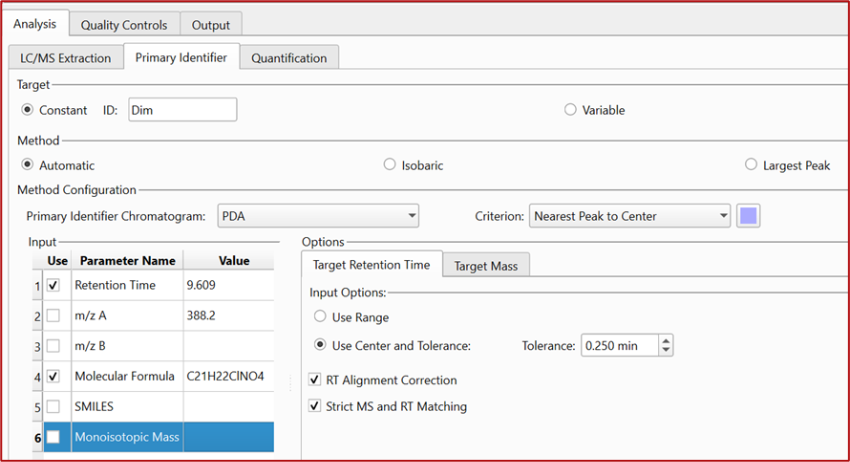
This enhancement also introduces a new method called “Isobaric,” which combines RT and m/z data to detect and assign the target peak while discarding isobaric interferences.
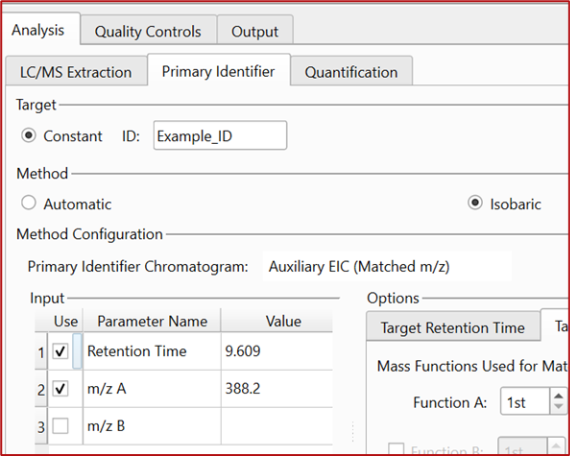

Support of Constant and Variable Targets
Chrom QC now gives you the flexibility to target a single constant across an entire batch or work with variable targets, streamlining identification and boosting efficiency in your workflows.

Improved Target Quantification and Impurity Analysis
Additionally, Chrom QC 2.0 enhances the quantification of the target compound in two key ways: first, by enabling the use of target-specific calibration files that support both linear and quadratic regression models and second, by providing reporting in Mgears Viewer on unknowns (impurities), see also section below on Mgears Viewer improvements.
Example of quantification for a constant target:
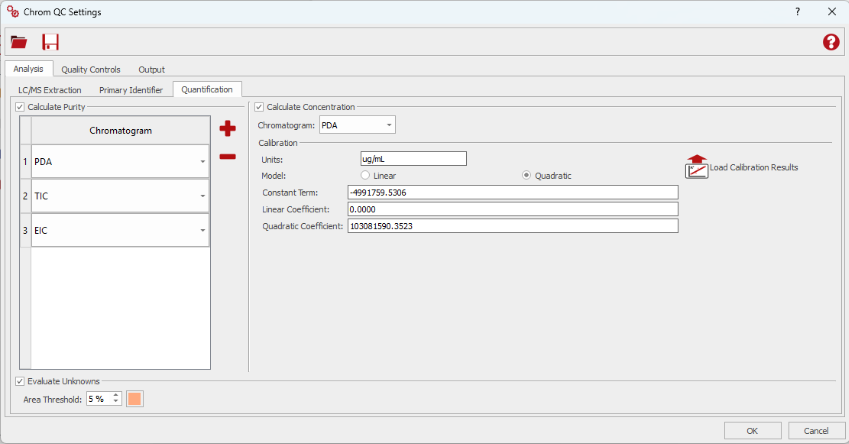
Example of quantification for variable targets:
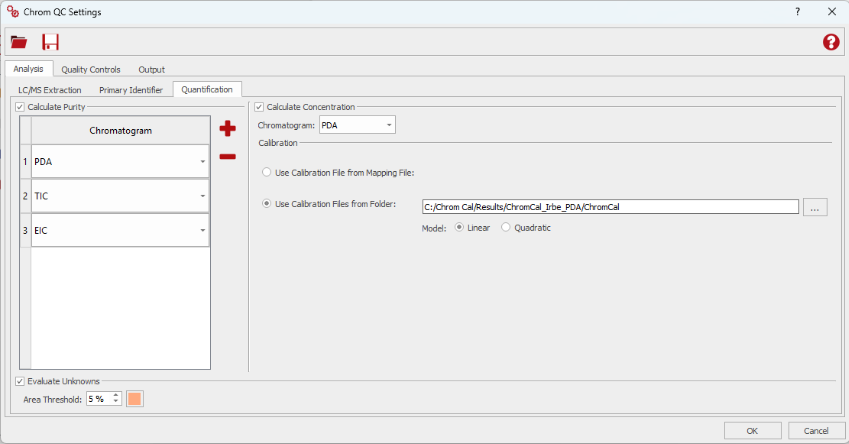
Enhanced Quality Control Parameters
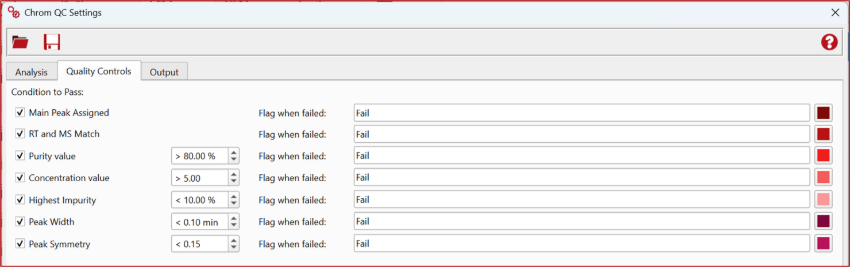
As Chrom QC 2.0 introduces more advanced methods for target detection, assignment, and quantification, users will notice the addition of new quality control features, including Peak Symmetry as a key parameter.
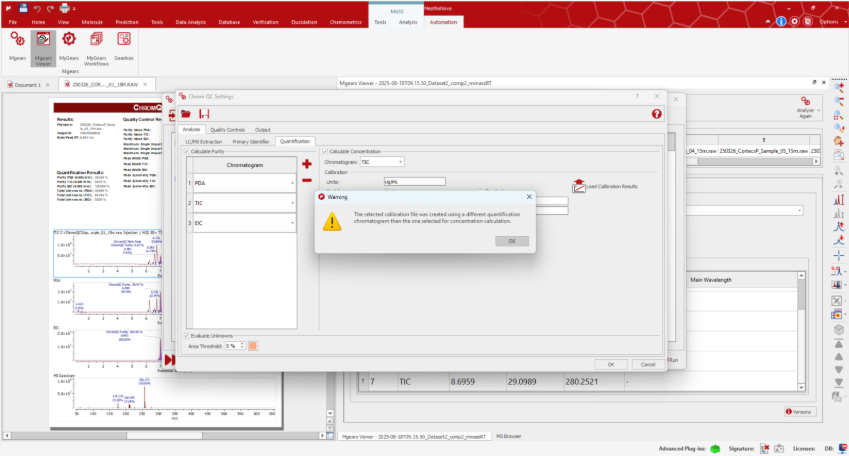
Helping Users Navigate and Troubleshoot
To support users in navigating the increased flexibility of these new features, the system now provides contextual warning and explanatory messages, helping users understand and resolve issues more efficiently.
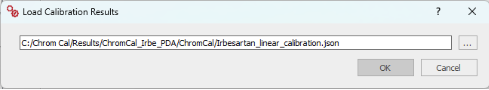
Example of a warning message displayed when loading a JSON file that contains a different quantification chromatogram than the one selected in ChromQC’s LC/MS extraction tab:
Results Improvements in Mgears Viewer
Detailed report of unknowns
ChromQC 2.0 introduces a powerful way to report unknown peaks: get a quick overview in the ‘Total Unknowns’ summary table, or dive into details in the ‘Detailed Unknowns’ tab, including retention time (RT), area percentage, and m/z or maximum wavelength for each peak.
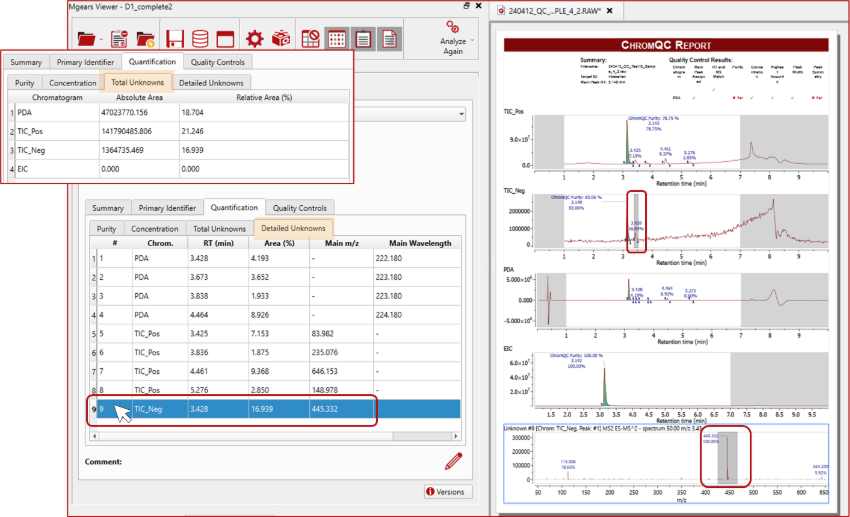
Addition of comments to sample results in Mgears Viewer
In this new version, besides the standard information recorded for each sample, you will also have the option to edit comments for individual samples, allowing you to add extra details or distinguish samples as needed.
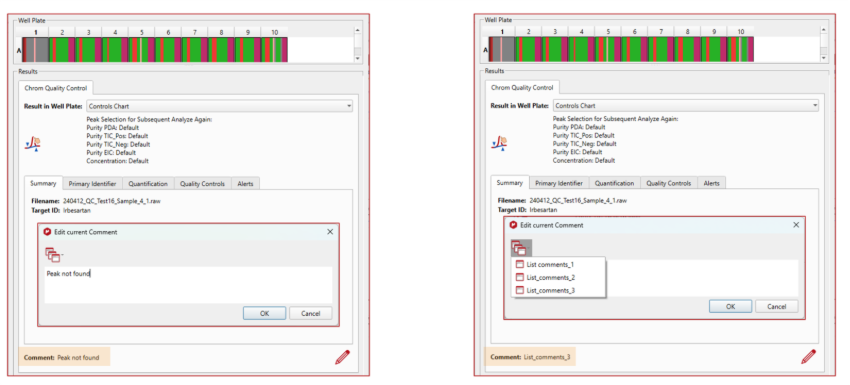
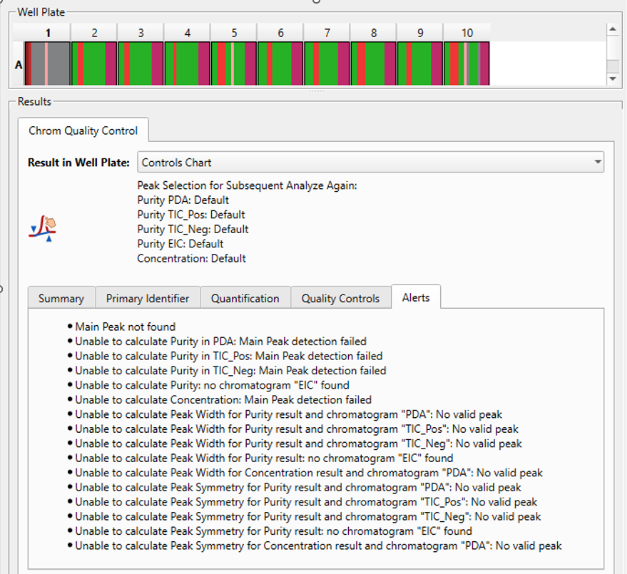
More insights, easier error reporting
This version of Chrom QC includes an improved results viewer, providing more information at a glimpse, a new and simpler method for error reporting.
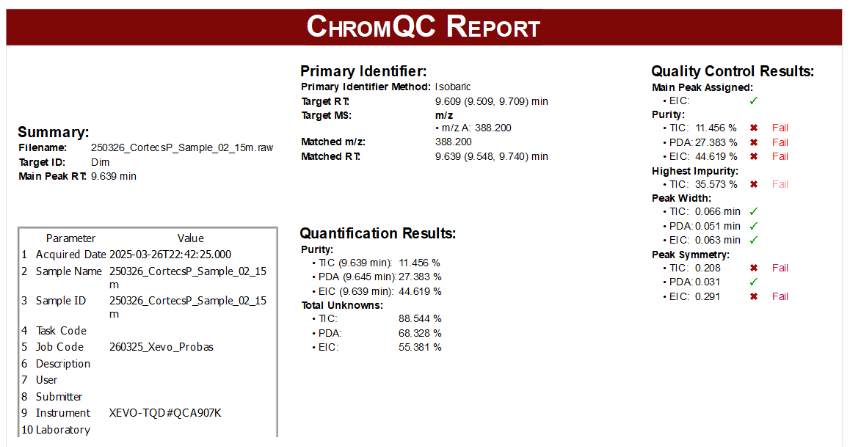
Enhanced configuration options for Mnova and CSV reports
Chrom QC 2.0 offers enhanced configuration options for Mnova, in addition to two new automatic report templates: Basic and Advanced, which will cover your standard and advanced reporting requirements.
Example of an advanced report, which includes per-default metadata, summary, primary identifier, quality control and quantification results:
Example of a basic report which includes per-default only a summary and
quality control results:

Ability to propagate manual selections across all samples
New manual peak selection tool that allows, as a new feature, to propagate a manual peak selection change across all samples.